Kali/ Raspberry pi/ Pihole+Unbound/ OMV/Docker/ Portainer - Notes
DISCLAIMER:
-
This document contains unedited notes and has not been formally
proofread.
-
The information provided in this document is intended to provide a
basic understanding of certain technologies.
-
Please exercise caution when visiting or downloading from websites
mentioned in this document and verify the safety of the website and
software.
-
Some websites and software may be flagged as malware by antivirus
programs.
-
The document is not intended to be a comprehensive guide and should not
be relied upon as the sole source of information.
-
The document is not a substitute for professional advice or expert
analysis and should not be used as such.
-
The document does not constitute an endorsement or recommendation of
any particular technology, product, or service.
-
The reader assumes all responsibility for their use of the information
contained in this document and any consequences that may arise.
-
The author disclaim any liability for any damages or losses that may
result from the use of this document or the information contained
therein.
-
The author reserve the right to update or change the information
contained in this document at any time without prior notice.
-
Any attempts to perform penetration testing or ethical hacking on
systems or networks should be done with the explicit permission of the
system/network owner. Unauthorized access is illegal and can result in
serious legal consequences.
-
It is important to fully understand the scope of the testing and to
only test within that scope. Testing outside the agreed upon scope is
considered unauthorized and may result in legal action.
-
Any findings or vulnerabilities discovered during testing should be
reported to the system/network owner immediately and kept confidential
until a fix can be implemented.
-
It is recommended to use a separate, dedicated testing environment
rather than testing on a live production system to minimize the risk of
accidentally causing damage or downtime.
-
It is important to take steps to protect your own identity and prevent
accidental data leaks or exposure of sensitive information during
testing.
-
It is also recommended to follow a standard code of ethics for ethical
hacking and penetration testing.
REFERENCES:
-
https://www.kali.org/tools/
-
https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/manual/grub/html_node/Command_002dline-and-menu-entry-commands.html
-
https://developer-old.gnome.org/NetworkManager/stable/nmcli.html
-
https://forum.greenbone.net/
-
https://docs.pi-hole.net/guides/dns/unbound/
-
https://www.youtube.com/@KMDTech
**************************************************************
This blog article covers:
-
It explores the various tools available in Kali Linux, a popular
operating system used for cybersecurity and penetration testing.
-
Dual booting Kali Linux with Windows:
-
It provides a guide on how to install and set up Kali Linux alongside
Windows, allowing users to choose between the two operating systems
during startup.
-
Building a NAS using Raspberry OS Lite:
-
It explains the process of creating a Network Attached Storage (NAS)
system using Raspberry Pi with the lightweight Raspberry OS Lite
operating system.
-
It explains how you can set up network-wide ad blocking using your
own Linux hardware. The Pi-hole is a DNS sinkhole that helps protect
your devices from unwanted content, all without the need to install
any software on individual devices.
-
VNC Virtual mode Along with OMV
-
These steps enable you to install a basic virtual desktop environment
on a headless Raspberry Pi Lite with OpenMediaVault. This allows you
to access the desktop using a VNC viewer.
************************************************
Contents:
-
DUAL Boot Kali Linux with Windows
-
Scanning networks on monitor mode
-
Configuring NAS (Network Attached Storage) on Raspberry Pi
-
Install OMV - openMediaVault
-
How to Change DNS in Kali Linux
-
Setting up VNC Server with OMV on Raspberry Pi Lite (Headless)
-
How to connect from Kali to Raspberry- Pi using
VNC-viewer

|
|
Missing X server or $DISPLAY-RealVNC Viewer
|
**************************************************************
Update the kali with complete Distribution upgrade:
-
sudo apt update
-
sudo apt upgrade
-
sudo apt full-upgrade -y
-
sudo apt dist-upgrade -y
Same on windows equivalent
PS C:\Users> winget.exe upgrade --all --include-unknown
How to Get Hostname and version of linux
- hostnamectl
- lsb_release -a
- cat /etc/os-release
- external ip address
- $ curl ifconfig.me
Search a command to install from CLI:
:~ $ apt search hwinfo
Sorting... Done
Full Text Search... Done
backupninja/oldstable,oldstable 1.2.1-1 all
lightweight, extensible meta-backup system
forensics-extra/oldstable,oldstable 2.29 all
Forensics Environment - extra console components
(metapackage)
hwinfo/oldstable 21.72-1 arm64
Hardware identification system
libhd-dev/oldstable 21.72-1 arm64
Hardware identification system library and headers
libhd-doc/oldstable,oldstable 21.72-1 all
Hardware identification system library documentation
libhd21/oldstable 21.72-1 arm64
Hardware identification system library
:~ $ sudo apt install hwinfo
Kali Linux : Boot loop error
To enter in to terminal window use :- Ctrl+ALT+F1
Now check the user under .Xauthority & .ICEauthority,
it should be user:user not as root:root
-
kali@kali: sudo chown kali:kali .Xauthority
-
kali@kali: sudo chown kali:kali .ICEauthority
-
kali@kali: reboot
Now the login should work.
Mount a Network folder on Linux
-
Sudo apt install cifs-utils
-
sudo mkdir /mnt/nwshare
-
sudo mount -t cifs //10.0.0.1/share /mnt/nwshare
-
prompt to enter the network password.
**************************************************************
DUAL Boot Kali Linux with Windows
When Windows option is missing from GRUB boot menu after installing Kali
Linux as Dual boot, follow below steps
##Run update & upgrade command
Run os-prober
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo os-prober
/dev/sda1:Windows
Run update-grub
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo update-grub
Just uncomment the below command
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo nano /etc/default/grub
#GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER=false
Once again Run update-grub
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo update-grub
Generating grub configuration file
...
done
Found Windows
Now Just reboot.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ reboot
Windows 11 Update Broke Dual Manager: FIX
After so many trial and error these steps worked to fix the GRUB dual
boot manager.
Step 1:
Using a bootable USB Drive - ventoy
Downloading latest - "Super GRUB2" from "supergrubdisk org" file to
discover the boot file and boot into Linux Distro.
Step 2:
After logging into Linux Distro, next updating the grub from terminal
window
:$> fdisk -l
/dev/sda1 EFI System
/dev/sda4 Linux filesystem
/dev/sda5 Microsoft basic data
Now Mounting the Linux file system partition & EFI boot
partition
- :$> mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/boot/efi
-
:$> for i in /dev /dev/pts /proc /sys /run; do mount -B $i
/mnt$i; done
-
grub-install: waring EFi variables cannot be set on this
system
Mounting the EFI parameters
- :$>mount -t efivarfs none /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
Verifying the boot file list
**************************************************************
GVM: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager
##Run update & upgrade command
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo apt install gvm
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo gvm-setup
[+] Done
[*] Please note the password for the admin user
[*] User created with password '**********************.
[>] You can now run gvm-check-setup to make sure everything is
correctly configured
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo gvm-check-setup
It seems like your GVM-22.4.1 installation is OK.
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ ss -lnt4
[>] Please wait for the GVM services to start.
[>] You might need to refresh your browser once it opens.
[>] Web UI (Greenbone Security Assistant):
https://127.0.0.1:9392
ob for gvmd.service failed because a timeout was exceeded.
See "systemctl status gvmd.service" and "journalctl -xeu
gvmd.service" for details.
ERROR:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo gvm-setup
[>] Starting PostgreSQL service
[-] ERROR: No PostgreSQL version uses the port 5432/TCP
[-] ERROR: libgvmd needs PostgreSQL 17 to use the port 5432
[-] ERROR: Use pg_upgradecluster to update your PostgreSQL cluster
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo pg_lsclusters
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo pg_dropcluster 16 main --stop
No PostgreSQL version uses the port 5432/TCP
-
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/17/main/postgresql.conf
-
edit the port number to reflect 5432
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo nano /etc/postgresql/17/main/postgresql.conf
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo systemctl restart postgresql
How to change Admin password in GVM:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo runuser -u _gvm -- gvmd --user=admin
--new-password=new-password
How to Update GVM feed
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo gvm-feed-update
Sudo greenbone-feed-sync
Verify GVM certificates
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ gvm-manage-certs -V
GVM Report Dashboard
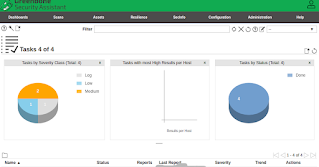
|
|
GVM dashboard
|
GVM PostgreSQL Collation Error:
The template database was created using collation version 2.36,
but the operating system provides version 2.37
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo -u postgres psql
could not change directory to "/home/kali": Permission
denied
psql (15.3 (Debian 15.3-0+deb12u1))
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# postgres=# ALTER DATABASE template1 REFRESH COLLATION
VERSION;
Note:changing version from 2.36 to 2.37
**************************************************************
Nessus
To access detailed information, refer to the topic "Scanning with Nessus"
within the Pentesting- Hands-on article.
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ sudo dpkg -i Nessus-10.5.1-debian10_amd64.deb
- You can start Nessus Scanner by typing /bin/systemctl start
nessusd.service
- Then go to https://kali:8834/ to configure your scanner
Testing/ ***************
-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
-
└─$ /bin/systemctl start nessusd.service
**************************************************************
WiFi
Reference :
https://developer-old.gnome.org/NetworkManager/stable/nmcli.html
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmcli general
STATE CONNECTIVITY WIFI-HW WIFI
WWAN-HW WWAN
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmcli connection show
NAME
UUID
TYPE
DEVICE
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmcli radio wifi off
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmcli radio wifi on
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmcli device wifi list
Connect to a password-protected wifi network
$ nmcli device wifi connect "$SSID" password "$PASSWORD"
Bluetooth:
sudo systemctl start bluetooth.service
**************************************************************
GREP command
Nmap : using Grep to filter IP addresses
Syntax : cat ip.txt | grep "text to search" | cut -d"" -f 2 | sort |
uniq
-
-f is the field like 2nd string or 11th string
and
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ cat ip.txt | grep -e "Status: Up"
- Host: 192.168.1.1 () Status: Up
- Host: 192.168.1.4 () Status: Up
- Host: 192.168.1.17 () Status: Up
- Host: 192.168.1.20 () Status: Up
- Host: 192.168.1.22 () Status: Up
- Host: 192.168.1.250 () Status: Up
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmap -T4 -A 192.168.1.0/24 -oG ip.txt
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ cat ip.txt | grep -e "Status: Up" | cut -d " " -f2
192.168.1.1
192.168.1.4
192.168.1.17
192.168.1.20
192.168.1.22
192.168.1.250
How to get URL list from www.website.com/sitemap.html
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ grep -Po 'http(s?)://[^ \"()\<>]*'
gouti1454URL.txt
http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9
https://www.gouti1454.com/p/kali-linux-hands-on.html
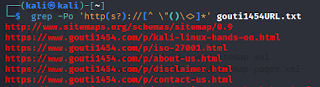
|
|
grep_url_sitemap_01
|
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ cat gouti1454URL.txt| grep -Po 'http(s?)://[^
\"()\<>]*'
http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9
https://www.gouti1454.com/p/kali-linux-hands-on.html

|
|
grep_url_sitemap_02
|
How to search the History of commands on linux
history | grep compose

|
|
history | grep compose
|
**************************************************************
Configuring VPN to remain anonymous while performing
Pentesting:
SOCKS5 get more anonymous identity
Sudo nano /etc/proxychains4.conf
Just delete the # from dynamic_chain
Add # on strict_chain
Restarting the network service
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo nano /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf
manager=true
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo service NetworkManager restart
Adding open source vpn accounts to kali
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo apt install network-manager-openvpn -y
└─$ sudo apt install network-manager-pptp -y
sudo apt install network-manager-openvpn -y
sudo apt install network-manager-pptp -y
sudo apt install network-manager-pptp-gnome -y
sudo apt install network-manager-strongswan -y
sudo apt install network-manager-vpnc -y
sudo apt install network-manager-vpnc-gnome -y
Changing MAC address no to get banned, while performing pentest
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ macchanger --help
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ macchanger wlan0 -s
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo macchanger -r wlan0
**************************************************************
Scanning networks on monitor mode
Placing your wifi network into monitor mode
ifconfig wlan0 down
iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor
ifconfig wlan0 up
sudo airmon-ng check
Killing the process which will interfere with monitor mode
sudo kill 555
sudo kill 699
sudo airmon-ng check
sudo service NetworkManager restart
Just to check what are the connected devices on the open wifi
networks
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo airodump-ng wlan0
*****************************************************
A step-by-step guide on how to install NAS (Network Attached
Storage) on a Raspberry Pi. It also explains how to use
Openmediavault to create shared folders for easy file sharing.
Additionally, the tutorial shows how to set up NordVPN Meshnet to
securely access the NAS over the internet.
Step 1:
-
Raspberry Pi Imager-installer:
-
use setting to add wifi network & Enable SSH
-
select Enable SSH then create the user as "pi" &
password.
Step 2:
-
Insert the image written SD card
-
Boot rasp-Pi and get he ip address
-
PC settings- Apps -> Optional Features -> Add on
optional features - search for open ssh client & open SSH
server
-
from PC terminal type ssh username@10.10.0.1
- ssh pinas@10.10.1.5
-
ssh kali@10.10.1.131
-
enter the password used while writing the os.
Step 3:
-
Now Updating then Upgrading rasp-Pi
-
Install OMV - openMediaVault
-
sudo wget -O -
https://github.com/OpenMediaVault-Plugin-Developers/installScript/raw/master/install
| sudo bash
Step 4:
-
Need to configure WiFi after installing OMV
- sudo omv-firstaid
- after installing OVM
-
Click on Configure Network interface and set up the SSID and
Password
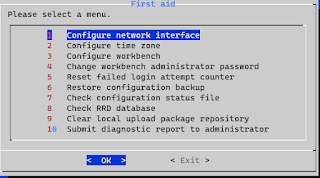
|
|
omv-firstaid
|
Step 5:
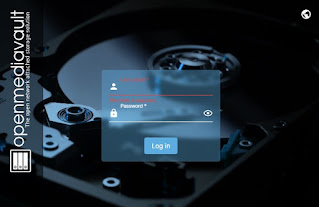
|
|
Login openMediaVault
|
-
Change in Default Password
- Storage -> disk

|
OMV_Disks
|
-
Storage -> File System
-
Click New -> file system then select the mounted HDD

|
|
OMV-file system
|
-
Storage -> Shared folders
-
Click Create ->Shared folder name
- Services
- Enable SMB
-
Shares - select the share folder created earlier

|
|
Services
|
- Users
-
Edit the password for the users
- PC
-
Right click and select add network folder

|
|
OpenMediaVault Dashboard - desktop
|
Remove Shared folders from OMV
-
Delete share folders listings
-
First deleted the shared folders from Services- SMB, then
NFS
-
Then, Storage ->shared files
-
Next edit the config file to eliminate internal
error
-
sudo nano /etc/openmediavault/config.xml
-
search for mntent and remove the tag <mntent> ...
</mntent>
-
sudo omv-salt deploy run fstab
-
sudo nano
/etc/monit/conf.d/openmediavault-filesystem.conf
-
clear any identical references to
dev-disk-by-label-NAME
-
Now deploy the changes from OMV
Install Plex
-
sudo apt install apt-transport-https
-
echo deb https://downloads.plex.tv/repo/deb public main |
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/plexmediaserver.list
-
curl https://downloads.plex.tv/plex-keys/PlexSign.key | sudo
apt-key add -
-
sudo apt install plexmediaserver
-
sudo systemctl start plexmediaserver
-
sudo systemctl enable plexmediaserver
-
sudo service plexmediaserver status
-
Add the created shared folders
-
-> secured connections - preferred
-
-> strict TLS configuration
-
Access Plex going forward
on https://app.plex.tv/desktop/
Setting Up NordVPN
reference article:
https://meshnet.nordvpn.com/how-to/remote-files-media-access/remote-openmediavault-nas
Step 1: Installing Nordvpn on NAS -raspberry pi.
-
root@pi: sh <(wget -qO -
https://downloads.nordcdn.com/apps/linux/install.sh)
-
root@pi:nordvpn login --token <paste the token generated
from NORDVPN account>
-
root@pi: nordvpn set meshnet on
-
root@pi: nordvpn meshnet peer list
Step 2:
Installing Nordvpn app on the device, which the NAS can be
accessed.
-
Type the meshnet name assigned:
-
eg - http://secret.meerkat-alps.nord/

|
|
OMV-via NORD from Mobile
|
-
eg - http://secret.meerkat-alps.nord:32400/

|
|
Plex - via NORD from Mobile
|
-
To access shared drive directly on android
-
File manager -> Network storage -> SMB
-
nordVPN- IP-address/Shared-Folder-name
-
Allowed User Id /Password
Enable Firewall on NAS
-
Command may disrupt existing ssh connections. Proceed
with operation (y|n)? y
-
Firewall is active and enabled on system
startup
-
sudo ufw status verbose or
-
Default: deny (incoming), allow (outgoing), disabled
(routed)
-
Firewall stopped and disabled on system startup
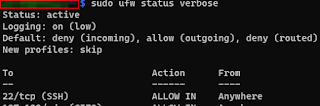
|
|
ufw status verbose
|
Can allow to have SSH tunnel connection to the
NAS server and Plex server on port 32400. NordVPN
is added by default.
-
sudo ufw allow 'www full'
The lsof (list open files) command returns the
user processes that are actively using a file
system
|
|
Plex local connection after firewall
|
Headless Console Font Size
To increase the font size on the console terminal of
the headless OS
-
sudo dpkg-reconfigure console-setup
-
Guess optimal character set
Installing Pi-Hole
This explains how you can set up network-wide ad blocking using
your own Linux hardware. The Pi-hole® is a DNS sinkhole that
helps protect your devices from unwanted content, all without
the need to install any software on individual devices.
-
Installation
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo curl -sSL https://install.pi-hole.net
| bash
-
Change Password for web interface
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ pihole -a -p
In an important step, if port
80 is already being used by another server, the Pi-hole needs to
be moved to a different port. This can be done by making changes
to the "/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf" file.
-
raspi:~ $ sudo cat /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
-
update the above server port to your choice
-
raspi:~ $ sudo cat /etc/lighttpd/external.conf
-
if required create and add same server.port =81
In the next step, you need to resolve any DNS conflicts by
editing the "/etc/systemd/resolved.conf" file. I want to
express my gratitude to YouTube channel "DBTechYT" for
providing helpful guidance on resolving this issue, which had
been a persistent challenge for over a week.
- raspi:~ $ sudo systemctl stop systemd-resolved
- raspi:~ $ sudo nano /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
- DNS=1.1.1.1 # adding values
- FallbackDNS=1.0.0.1# adding values
-
DNSStubListener=no # To ensure that the
system uses the values in this file, you need to add a
new line.
-
raspi:~ $ sudo ln -sf /run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf
/etc/resolv.conf
Pi-Hole V6 Errors:
Not to add internal loop address to interface that will
block the web-interface.
$:>pihole -d
Initializing HTTP server on ports
"80o,8443os,[::]:80o,[::]:8443os,192.168.1.5:81,127.0.0.1:80"
cannot bind to 127.0.0.1:80: 98 (Address in use)
:~ $ sudo cat /etc/pihole/pihole.toml
# Possible values are:
# comma-separated list of
<[ip_address:]port>
port =
"80o,8443os,[::]:80o,[::]:8443os,192.168.1.5:81,127.0.0.1:80"
### CHANGED, default = "80o,443os,[::]:80o,[::]:443os"
Manually removing the loop address from the above line,
allows the web interface to be online.
Pi-hole Ad blocking domains:
Add a new domain or regex filter:
-
diproton-ads-[^\.]*\.hulu\.com\.akadns\.net
-
https://github.com/hagezi/dns-blocklists?tab=readme-ov-file#pro
Pi-hole with Unbound
Finally, you need to install Pi-hole with Unbound, and it's
important to disable the "resolvconf.conf" entry for Unbound.
This step is necessary for Debian Bullseye+ releases.
https://docs.pi-hole.net/guides/dns/unbound/
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo apt install unbound
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo nano
/etc/unbound/unbound.conf.d/pi-hole.conf
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo service unbound restart
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ dig pi-hole.net @127.0.0.1 -p 5335
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ systemctl is-active
unbound-resolvconf.service
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo cat
/etc/unbound/unbound.conf.d/resolvconf_resolvers.conf
-
# Generated by resolvconf
-
- forward-zone:
-
name: "."
-
forward-addr: 10.10.1.1
-
forward-addr:
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo sed -Ei
's/^unbound_conf=/#unbound_conf=/'
/etc/resolvconf.conf
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo rm
/etc/unbound/unbound.conf.d/resolvconf_resolvers.conf
-
pinas@raspi:~ $ sudo service unbound restart
-
raspi:~ $ sudo cat /etc/resolv.conf
-
update the nameserver to pihole and 1.1.1.1
UFW Firewall Rules:
If you have enabled the firewall, you can add the port to the
allow list by running the command
When these rules are not added, pi-hole will fail to have any
clients other than internal IP's.
ufw stores all rules persistent, so you just need to
execute the commands below.
https://docs.pi-hole.net/main/prerequisites/
-
ufw allow 80/tcp
-
ufw allow 53/tcp
-
ufw allow 53/udp
-
ufw allow 67/tcp
-
ufw allow 67/udp
-
ufw allow 546:547/udp
OMV :
http://10.10.1.5/#/dashboard
Portainer :
https://10.10.1.5:9443/#!/home
Plex : http://10.10.1.5:32400/web/index.html#!/
Pi-hole : http://10.10.1.5:81/admin/index.php

|
|
Pi-hole
|
How to Change DNS in Kali Linux
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo cat /etc/resolv.conf
# Generated by NetworkManager
nameserver 10.0.0.1
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo nano /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 10.0.0.5 #pi serverip address
Now the resolv.conf is made as only readable mode.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo chattr +i /etc/resolv.conf
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
If want to edit the resov.conf file once again
:-
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo chattr -i /etc/resolv.conf
Setting up VNC Server with OMV on Raspberry Pi Lite
(Headless)
These steps enable you to install a basic virtual
desktop environment on a headless Raspberry Pi Lite with
OpenMediaVault. This allows you to access the desktop
using a VNC viewer.
-
pi@raspi: sudo raspi-config
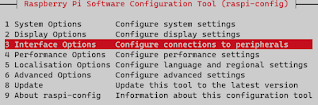
|
|
raspi-config
|
- Select the Interface and enable VNC
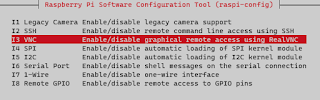
|
|
enable VNC
|
Installing VNC server and if required vnc viewer
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt-get install
realvnc-vnc-server
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt-get install
realvnc-vnc-viewer
-
pi@raspi: sudo systemctl start
vncserver-x11-serviced.service
-
pi@raspi: sudo systemctl enable
vncserver-x11-serviced.service
-
pi@raspi: sudo systemctl status
vncserver
-
if the service doesn't start try to kill any
early started services
-
kill running process if any.
-
pi@raspi: sudo netstat -ptnl | grep
vnc
-
pi@raspi: sudo systemctl start vncserver
-
pi@raspi: sudo systemctl status
vncserver.service
-
New desktop is raspberryi:1 (10.0.0.1:1)
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt-get clean
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt-get install lxde-core
lxappearance
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt-get install xterm
Start VNCviewer and key in the address
10.0.0.1:1

|
|
VNC viewer
|
Vnc Viewer : access denied error
-
"Access denied error" occurs, follow below
steps,
-
pi@raspi: vncserver-virtual
-
[Don't use Sudo- root user is not added in
"users & permissions" by default under
RealVNC server settings]
-
pi@raspi: sudo systemctl restart
vncserver.service
-
pi@raspi: sudo systemctl status
vncserver.service
-
Raspi username and password
-
where authentication is set to VNC
password. [refer image - raspi vnc security
settings-on]
-
no username - the user name is greyed
out
-
password - use vnc password - changed in
the vnc connect window
You can install the
Chromium browser on the VNC virtual
desktop,
which allows you to perform the same operations as
logging into the OMV admin page and Pi-hole admin
page.

|
|
Chromium browser
|
The VNC virtual desktop on Raspberry Pi with
OpenMediaVault (OMV) has a simple interface. It is
crucial to avoid installing lightdm as it will
uninstall OMV from your Raspberry Pi and cause it to
crash.
After a few attempts and some exploration, I was able
to find more usable fonts and apps.
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt install
xserver-xorg-core
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt install
xserver-xorg-video-fbdev
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt install
xserver-xorg-input-evdev
-
pi@raspi: sudo apt install xinit xfonts-base
lxde

|
|
Updated icons themes
|
Now, you may connect to the Raspberry Pi NAS from
an Android device using the NordVPN Meshnet IP
address without a computer or monitor.
2025: Setting up VNC Server with OMV on
Bookworm- Raspberry Pi Lite (Headless)
After Several
hours of trial and error method only
"tightvncserver" works well with headless Pi
image.
Was
trying earlier with
"realvnc-vnc-server realvnc-vnc-viewer", which
resulted in errors like:-
-
could not connect to vnc server. please
ensure that you have the required licence
for this feature.
-
vnc server cannot currently show the
desktop.
These are the commands, helped to achieve the
barebone "lxde" desktop environment.
sudo raspi-config
- Select the Interface and enable VNC
-
Display option -> VNC resolution ->
select highest value
Installing Tightvncserver
-
sudo apt install lxde-core tightvncserver
-
sudo apt-get install xfonts-base
- sudo apt install xserver-xorg-core
-
sudo apt install xserver-xorg-video-fbdev
-
sudo apt install xserver-xorg-input-evdev
- sudo apt install xinit xfonts-base
-
sudo apt install --reinstall lxterminal
- sudo apt install lxpanel
- sudo apt install lxappearance
- sudo apt install -y lxde-core xrdp

|
|
lxde -desktop on Headless Pi
|
How to connect from Kali to Raspberry- Pi
using VNC-viewer
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo vncviewer 10.0.0.1:1
no configured security type is supported by 3.3
vnc viewer
If you encounter the error mentioned above, you
can resolve it by applying the following
solution.

|
|
raspi VNC security settings-on
|
-
open the VNC Connect window from above virtual
desktop,
-
Click on the hamburger menu
-
Encryption = Preferred on
-
Authentication = VNC password
-
A Pop-up window appears
-
Now click Configure to key in new
Password
-
select the checkbox - Allow connections from
legacy VNC viewers.
When attempting to launch VNC Viewer from Kali,
the output displayed was as follows:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo vncviewer 10.0.0.1:1
-
password - use vnc password - changed in the
vnc connect window
-
Connected to RFB server, using protocol
version 3.3
-
Performing standard VNC
authentication
-
Password:
-
Authentication successful
-
Desktop name "****************"
-
VNC server default format:
-
32 bits per pixel.
-
Least significant byte first in each
pixel.
-
True colour: max red 255 green 255
blue 255, shift red 16 green 8 blue 0
-
Using default colormap which is
TrueColor. Pixel format:
-
32 bits per pixel.
-
Least significant byte first in each
pixel.
-
True colour: max red 255 green 255
blue 255, shift red 16 green 8 blue 0

|
|
Kali Vnc-viewer
|
**************************************************************
https://www.tecmint.com/iptraf-ng-linux-network-monitoring/
Docker
https://docs.portainer.io/start/install-ce/server/docker/linux
https://docs.linuxserver.io/general/docker-compose/
Portainer:
pinas@pi:$ docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 9443:9443 --name=portainer
--restart=always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v
portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer-ce
How to Run Browser in Docker Container
https://github.com/jlesage/docker-firefox
https://hub.docker.com/r/jlesage/firefox
pinas@pi:$ docker run -d --name=firefox -p 3000:3000 -p 3001:3001
--restart unless-stopped lscr.io/linuxserver/firefox:latest

|
|
Browser on Docker
|
**************************************************************
Pi-Alert Using Pi-Hole
Scanning Local network for connected devices, using Pi-Alert
Leiweibau/Pi.Alert
-
https://github.com/leiweibau/Pi.Alert
-
curl -sSL
https://github.com/leiweibau/Pi.Alert/raw/main/install/pialert_install.sh
| bash
-
curl -sSL
https://github.com/leiweibau/Pi.Alert/raw/main/install/pialert_uninstall.sh
| bash

|
|
Dashboard : Leiweibau/Pi.Alert
|
Pucherot/Pi.Alert
Last update 3years:
-
https://github.com/pucherot/Pi.Alert
-
curl -sSL
https://github.com/pucherot/Pi.Alert/raw/main/install/pialert_install.sh
| bash
-
curl -sSL
https://github.com/pucherot/Pi.Alert/raw/main/install/pialert_uninstall.sh
| bash

|
|
Dashboard: Pucherot/Pi.Alert
|
Jokob-sk/NetAlertX
-
https://github.com/jokob-sk/NetAlertX
***********************************************************
Previous steps covered installing OMV on a headless Raspberry Pi.
Now, enabling Docker Compose on OMV7 and setting up containers from
OpenMediaVault.
Step 01: Enabling Docker repo
OMV -> System -> omv-extras -> check the box, then
save.

|
| OMV |
Step 02: Installing OMV-compose & plugins
OMV -> System -> Plugins
Search for the plugins, then click install icon :
openmediavault-compose
openmediavault-scripts

|
|
search for openmediavault
|
Now access Docker Compose under the hamburger menu

|
|
Docker compose menus appearing
|
Step 03: Creating Shared folder structure
Now Services -> Compose -> Settings
Next step is to add share folders for
Compose Files
Data
Backup
Now need to create share folders for the above
Click -> add then provide
Name
Filesystem
then save it

|
|
shared folder
|
Now going back to Services -> Compose -> Settings
To add the shared folders

|
|
share folders added to compose settings
|
Step 04: Now Creating Docker Compose File to create containers.
Creating a User for Docker:
Give a name, then add the user to the groups and then check the box
for: disallow docker user account
Services ->Compose->Files
adding the code
services:
tor:
image: domistyle/tor-browser
container_name: tor-browser
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
- TZ=Etc/UTC
volumes:
- /data/config:/config
ports:
- 9900:9900
- 9800:9800
restart: unless-stopped
Now need to replace the volume path
Just copy the path of the data shared folder created
earlier
e.g replace /path/to alone.
/data/config:/config
Then -> Click Save
Next Click up button to initiate docker compose up
command

|
|
UP button
|
Now the container is deployed and ready to access
using

|
|
Docker Container deployed
|
*****************************************************************************
Home Assistant on OMV Container
Reference : https://www.home-assistant.io/installation/linux
Install Home Assistant Container
OMV->Services->Compose->Files->add

|
|
Home Assistant container
|
services:
homeassistant:
image: ghcr.io/home-assistant/home-assistant:stable
container_name: homeassistant
network_mode: host
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
- TZ=Etc/UTC
volumes:
- /data/homeassistant/data:/config
ports:
- 8123:8123 #optional
restart: unless-stopped
Once the container is up and running, following the onboarding
steps.
https://www.home-assistant.io/getting-started/onboarding/
How to Add Tapo Cameras
https://github.com/JurajNyiri/HomeAssistant-Tapo-Control?tab=readme-ov-file
Step1:
Enabling Third party support in the Tapo app.
Me->Tapo lab->Third-party-compatibility
Step2
For each camera, need to enable camera username and password
Step 3:
Adding -> TP-Link integration in Home Assistance
Step 4:
For live streaming, use Onvif Integrations
Give IP address of the camera and port as 2020

|
|
HA dashboard
|
Adding integrations
Installing hacs-integration
https://hacs.xyz/docs/use/download/download/#to-download-hacs-container
pi@piraspi:~> sudo docker exec -i -t 1c4f56c6fe802 bash
wget -O - https://get.hacs.xyz | bash -
************************************************************
Raspberry Pi Connect
The Raspberry Pi Connect - Lite enables the Raspi-Lite OS to establish
remote connections via SSH shell.
:~ $ sudo apt install rpi-connect-lite
:~ $ rpi-connect on
:~ $ rpi-connect signin
Complete sign in by visiting
https://connect.raspberrypi.com/verify/xcrtfyuvfjgf
✓ Signed in

|
|
Connect raspberry
|
Enable remote shell at all times
$: rpi-connect shell on
$: loginctl enable-linger

|
|
Remote SSH shell
|
************************************************************
Jellyfin On Container
https://jellyfin.org/docs/general/installation/container
The docker compose file details are below,
-
The volume must be mapped correctly to reflect the shared folder
created in the NAS. There are two different ways listed to
map.
-
The volume path can be copied from the absolute path displayed,
under OMV-> Storage->Shared Folders
services:
jellyfin:
image: jellyfin/jellyfin
container_name: jellyfin
network_mode: 'host'
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
- TZ=Etc/UTC
volumes:
- /data/config:/config
- /data/cache:/cache
-
/srv/dev-disk-by-uuid-skghfdkjh7/NAS:/data/movies
- type: bind
source:
/srv/dev-disk-by-uuid-skghfdkjh7/NAS
target: /media
read_only: true
restart: 'unless-stopped'
extra_hosts:
- 'host.docker.internal:host-gateway'
To Access JELLYFIN outside the local network
https://jellyfin.org/docs/general/networking/
Following the steps to create Self-Signed Certificate
Self-Signed Certificate
SHH into the container, then execute the following
commands.
:~ $ sudo docker exec -i -t eyh5h7fh493j sh
-
# openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout ./privkey.pem -out
cert.pem -days 365 -nodes -subj '/CN=jellyfin.lan'
Enter
PEM pass phrase: Verifying - Enter PEM pass phrase:
Omit -nodes to set a password interactively.
Remove -days 365 to make it 'permanent'.
Add -subj '/CN=localhost' to make it not ask interactive questions
about content of certificate.
The above command creates ./privkey.pem which will require one more
step before use in Jellyfin.
-
openssl pkcs12 -export -out jellyfin.pfx -inkey privkey.pem -in
cert.pem -passout pass:
Enter
pass phrase for privkey.pem:
Next step to add SSL certificate path
Next to add the NORDVPN MESHNET IP address
Last restating the container to take effect.
************************************************************
Portainer on OMV
Change to absolute path
: 'CHANGE_TO_COMPOSE_DATA_PATH/portainer/portainer_data:/data'
---
services:
portainer:
image: portainer/portainer-ce:latest
container_name: portainer
restart: unless-stopped
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
volumes:
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro
- /data/portainer/data:/data
ports:
- 9000:9000
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
http://192.168.1.5:9000/
************************************************************
**************************************************************
Installing VNC on a Linux Server: Final Working Method After
Multiple Attempts
Setting up a VNC server on a Linux machine can be straightforward,
but in some cases it takes several trials to get a stable desktop
environment without errors. After testing different combinations,
this final setup worked reliably and resolved all major issues.
This guide covers the steps, commands, and fixes that helped
achieve a fully working VNC environment using XFCE and TightVNC.
Common Errors Faced During Setup
These issues were encountered during the initial attempts:
- RealVNC server showing “Missing X server or $DISPLAY”
- Terminal not opening inside VNC
- Display manager not loading correctly
-
“Client is not authorized to connect to server & Cannot
open display 1.0”
First set of initial view commands to install VNC server to linux
server;
Install TightVNC and XFCE along with required dependencies.
- sudo apt install tightvncserver -y
-
sudo apt-get install xfce4 lightdm-gtk-greeter dbus-x11
autocutsel -y
- sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies lightdm -y
Second set of commands to troubleshoot terminal not working in VNC
Some installations cause the terminal window to fail.
Reinstall the terminal:
- sudo apt reinstall xfce4-terminal -y
Third step to reinstall one module at a time and these are optional
steps;
If certain desktop components misbehave, reinstalling related XFCE
modules can help.
- sudo apt reinstall xfce4-settings -y
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfce4-power-manager
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfce4-session
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfce4-notifyd
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfce4-panel
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfce4-whiskermenu-plugin
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfce4-indicator-plugin
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfce4-datetime-plugin
- sudo apt -y reinstall xfwm4-themes
Fourth step Changing display manager:
Changing the Display manager to slim & lightdm, to
troubleshoot the error - "Missing X server or $DISPLAY", while
opening a browser
step 4.1: change display manager:-
- sudo apt install slim -y
- sudo apt reinstall lightdm -y
- sudo dpkg-reconfigure lightdm
- # Select: lightdm
- sudo service lightdm start
Still the error was not resolved.
step 4.2: Next method - Update the VNC xstartup Configuration;
Open the xstartup file:
- $ sudo cat /home/serv4/.vnc/xstartup
- adding the below line to the file;
step 4.3 Next step - Installing X Support Packages
sudo apt install xvfb
sudo apt install xdg-utils
This resolved the display-related errors on the machine.
Finally step towards resolving the error - client is not authorized
to connect to server error cannot open display 1.0;
SSH in to the server :-
serv4@serv4:~$
serv4@serv4:~$ vncserver
New 'X' desktop is serv4:1
Starting applications specified in /home/serv4/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/serv4/.vnc/serv4:1.log
Then inside the VNC session terminal:
solution 1:
$ rm -rfv ~/.Xauthority*
$ brave &
Solution 2:
$ xhost +local:
$ brave &
This resolved the final display authorization issues, and the
browser launched correctly.

|
|
Missing X server or $DISPLAY-RealVNC Viewer
|
**************************************************************
Enabling VNC-server service at Boot
Step 01: Edit ~/.vnc/xstartup
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo cat ~/.vnc/xstartup
#!/bin/sh
xrdb "$HOME/.Xresources"
xsetroot -solid grey
#x-terminal-emulator -geometry 80x24+10+10 -ls -title
"$VNCDESKTOP Desktop" &
#x-window-manager &
# Fix to make GNOME work
# Start up the standard system desktop
export XKL_XMODMAP_DISABLE=1
/etc/X11/Xsession
startxfce4 &
Step02: Create vncserver@.service
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo cat
/etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service
[Unit]
Description=Start TightVNC server at startup
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=ser_g1454
WorkingDirectory=/home/ser_g1454
PIDFile=/home/ser_g1454/.vnc/%H:%i.pid
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i > /dev/null
2>&1
ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver -depth 24 -geometry 1280x800
:%i
ExecStop=/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Step03: Starting vncserver@.service
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo systemctl enable
vncserver@1.service
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ vncserver -kill :1
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo systemctl start vncserver@:1
sudo systemctl status vncserver@1
● vncserver@1.service - Start TightVNC server at
startup
Loaded: loaded
(/etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service; enabled;
preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo netstat -ptnl | grep vnc
tcp 0 0
0.0.0.0:6001
0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 1669/Xtightvnc
tcp 0 0
0.0.0.0:6002
0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 6757/Xtightvnc
Error: failed to start - systemctl start
vncserver@:1
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo crontab -e
@reboot vncserver no
***---***
Error: /system.slice/system-vncserver.slice/vncserver@1.service is
not a snap cgroup
While opening browser in VNC-viewer
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ sudo cat ~/.vnc/xstartup
#for vnc to open browsers
xhost +local:
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ chmod +x ~/.vnc/xstartup
next,
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ echo $DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS
unix:path=/run/user/1000/bus
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ echo $XDG_RUNTIME_DIR
/run/user/1000
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ export
DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS="unix:path=$XDG_RUNTIME_DIR/bus"
ser_g1454@servg1454:~$ brave &
***---***
Error's
Error: systemd-networkd-wait-online service timing out
during boot
sudo systemctl edit
systemd-networkd-wait-online.service
### Editing
/etc/systemd/system/systemd-networkd-wait-online.service.d/override.conf
### Anything between here and the comment below will
become the contents of the drop-in file
[Service]
ExecStart=
ExecStart=/usr/lib/systemd/systemd-networkd-wait-online
-i <relevant interface>
### Edits below this comment will be discarded
--- where <relevant interface> = eno1 or
wlp1s0
***---***
Error: audio not working
For Ubuntu/Debian-based Systems
# Remove core audio packages (use --purge for cleaner
removal)
sudo apt-get purge alsa-base pulseaudio pavucontrol
# Update package lists
sudo apt update
# Reinstall core audio packages
sudo apt install alsa-base pulseaudio pavucontrol
# Reboot your system
reboot
**************************************************************














Comments
Post a Comment